In the world of welding, the journey from novice to expert often begins with a registered apprenticeship. These programs offer aspiring welders the opportunity to learn the trade hands-on, under the guidance of experienced professionals called journeyworkers. However, gaining entry into a welding apprenticeship program requires meeting specific requirements.
In this article, we’ll delve into the essential aspects of welding apprenticeship requirements, shedding light on what it takes to embark on this rewarding career path.
Understanding Welding Apprenticeships
Before diving into the requirements, let’s grasp the concept of welding apprenticeships.
An apprenticeship is a structured training program that combines on-the-job training (often referred to as OJT) with classroom instruction in a college, often referred to as the related training or RTI provider.
It serves as a pathway for individuals to acquire the necessary skills and knowledge to become proficient welders while getting paid a living wage and earning a debt-free college degree. Read up on the amazing benefits of apprenticeships if you haven’t already.
In addition to registered apprenticeships (for college aged students), pre-apprenticeships for high school students are started to get launched across the country. You’ll need to see what your local public education system offers if you haven’t graduated from high school yet.
Essential Skills and Attributes
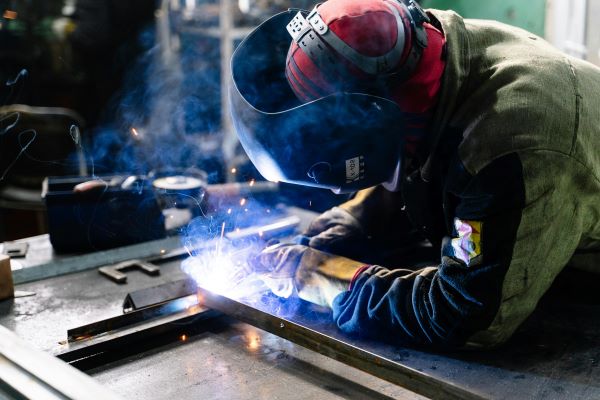

While the specific requirements may vary depending on the program and region, certain skills and attributes are universally valued in prospective welding apprentices:
- Manual Dexterity: Welding involves precise hand movements and coordination. Applicants should possess good manual dexterity to manipulate welding equipment effectively.
- Attention to Detail: The ability to pay close attention to detail is crucial in welding. A keen eye for precision ensures quality workmanship and safety compliance.
- Physical Fitness: Welding is a physically demanding profession. Applicants should be in good health and capable of standing for long periods, lifting heavy objects, and working in various positions.
- Mathematical Aptitude: Basic math skills are essential for measuring materials, calculating dimensions, and understanding blueprints and technical drawings.
- Problem-Solving Skills: Welders often encounter challenges that require quick thinking and problem-solving abilities. A logical approach to troubleshooting is highly valued in this field.
Expect to answer questions on your abilities when you apply to a program that is run within GoSprout’s apprenticeship management software.
Educational Requirements
While a high school diploma or equivalent is typically the minimum educational requirement for entering a welding apprenticeship at a local college, some programs may have additional prerequisites.
These may include:
- Math and Science Proficiency: Strong performance in math and science subjects, such as algebra, geometry, and physics, demonstrates the ability to grasp technical concepts essential for welding.
- Technical Training: Completion of vocational courses or pre-apprenticeship programs in welding can provide a solid foundation for aspiring welders.
Want to Learn More About Your Registered Apprenticeship Opportunities?
BOOK A FREE CONSULTATION
Certifications and Licenses
In addition to meeting educational and skill-based criteria, aspiring welders may need to obtain certain certifications and licenses to qualify for apprenticeship programs. These may include:
- Welding Certification: Some apprenticeship programs require applicants to hold industry-recognized welding certifications, such as those issued by the American Welding Society (AWS) or similar organizations.
- Driver’s License: A valid driver’s license may be necessary, especially if the apprenticeship involves travel to job sites or requires operating welding equipment.
Additional Considerations
Beyond the basic requirements outlined above, there are a few additional factors to keep in mind:
- Age Restrictions: Some apprenticeship programs may have minimum age requirements for applicants. Be sure to check the eligibility criteria before applying.
- Background Checks: Certain apprenticeships may require candidates to undergo background checks or drug screenings as part of the selection process.
- Interviews and Assessments: Candidates may be asked to participate in interviews or skills assessments to evaluate their suitability for the apprenticeship.
Conclusion
Embarking on a welding apprenticeship is a significant step towards building a rewarding career in the welding industry. By understanding and meeting the necessary requirements, aspiring welders can position themselves for success in these valuable training programs. Whether it’s honing technical skills, obtaining certifications, or demonstrating a commitment to safety and quality, meeting the welding apprenticeship requirements sets the stage for a fulfilling journey towards mastery in the art of welding.














